
Sun and Moon appear equally large, so the Moon covers the entire Sun – but only just. Imagine looking at the Sun from that spot. The spot where the 2 V-shaped shadows meet and the umbra turns into the antumbra marks the location where the apparent size of the Sun matches that of the Moon. Why Are Only Some Solar Eclipses Annular?Īnnular solar eclipse with “ring of fire.” For example, the annular solar eclipse on Februis only visible along a narrow belt stretching from southern Latin America to central Africa, and across parts of the South Pacific Ocean and the South Atlantic Ocean. Even during an annular solar eclipse, the antumbra only covers a small area on Earth.Īs both the Moon and the Earth are in constant motion, the antumbra moves across the face of the Earth during the eclipse, so the annular phase can usually only be seen along a slim eclipse path. The reason why annular solar eclipses are so rare is that the Moon's antumbra rarely hits the Earth's surface. This means that somewhere in space, on the dark side of the Moon, an annular solar eclipse is happening right now – unless there is a total solar eclipse in process as you read this.

That is the case during a total solar eclipse when the Moon's umbra falls on Earth. However, since the antumbra starts at a certain distance from the Moon, beyond the umbra, it does not form if the shadow hits a solid object within the umbra's range. Most of the time, it includes an antumbra. On its journey through space, the Moon always casts a shadow. If the antumbra falls on Earth, we can see an annular solar eclipse. Where they meet, the 2 shadow areas look a bit like an hourglass, if viewed from the side. In contrast to the umbra, the antumbra's diameter increases with growing distance from the Moon. If the umbra falls on Earth, we can see a total solar eclipse.Īs we move further away from the Moon, the umbra is followed by another V-shaped shadow. With growing distance from the Moon, the umbra's diameter decreases, creating a cone-shaped shadow core (see illustration).
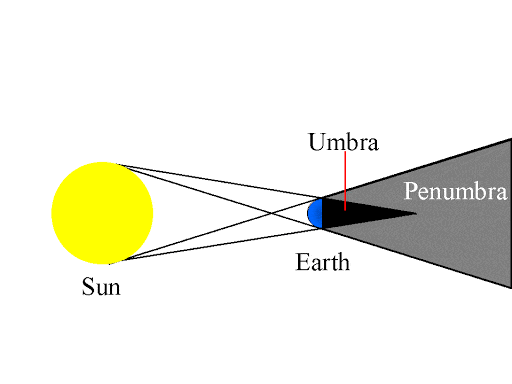
The core of the Moon's shadow consists of a dark center that is referred to as the umbra. The type of eclipse depends on the type of shadow that is involved.Īstronomical terms & definitions Causes Annular Solar Eclipses When the Earth enters the Moon's shadow, we see a solar eclipse when the Moon travels through the Earth's shadow, a lunar eclipse occurs.


Umbra – the shadow's dark center portion.For example, if you are in the antumbra during an annular solar eclipse, you can see the edge of the Sun's disk as a “ring of fire” around the Moon. In the antumbra, you will see the outer rim of the light source around the object casting the shadow. It only exists if the light source has a larger diameter than the object. The antumbra is the lighter area of a shadow that appears beyond the umbra, at a certain distance from the object casting the shadow. Each shadow has 3 different areas: the umbra, the penumbra, and the antumbra. Like any other opaque objects illuminated by a light source, the Moon and the Earth cast shadows into space as they block the sunlight that hits them. Business Date to Date (exclude holidays).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
